
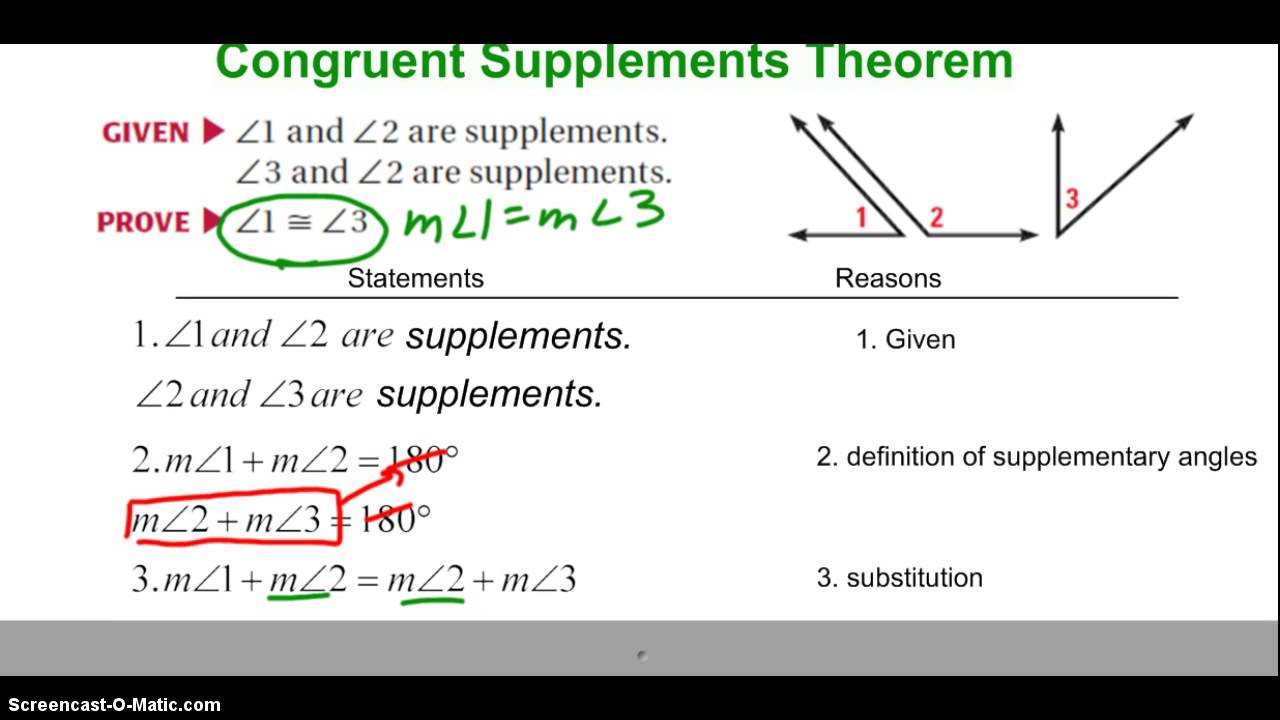
Such angles are called a linear pair of angles. have a common vertex and share just one side), their non-shared sides form a straight line. The supplementary angle theorem states that if two angles are said to be supplementary to the same angle, then the two angles are said to be congruent. If the two supplementary angles are adjacent (i.e. Supplementary angles are also classified as:-. Two angles that sum to a straight angle (1 / 2 turn, 180, or radians) are called supplementary angles.
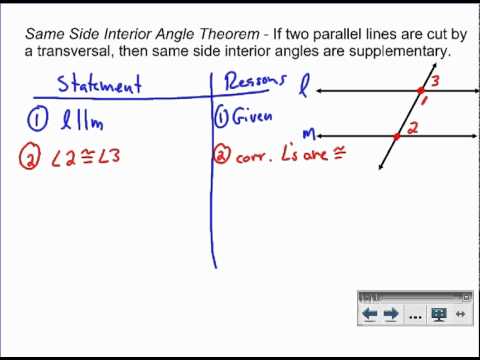
Theorem 2): If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the exterior angles on the same side of the transversal are supplementary angles. The two types of corresponding angles are:ġ) Corresponding Interior Angle: Found at the inner side of the intersection between the parallel lines and the transversal.Ģ) Corresponding Exterior Angle: Found at the outer side of the intersection between the parallel lines and the transversal. Theorem 1): If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the interior angles on the same side of the transversal are supplementary angles.
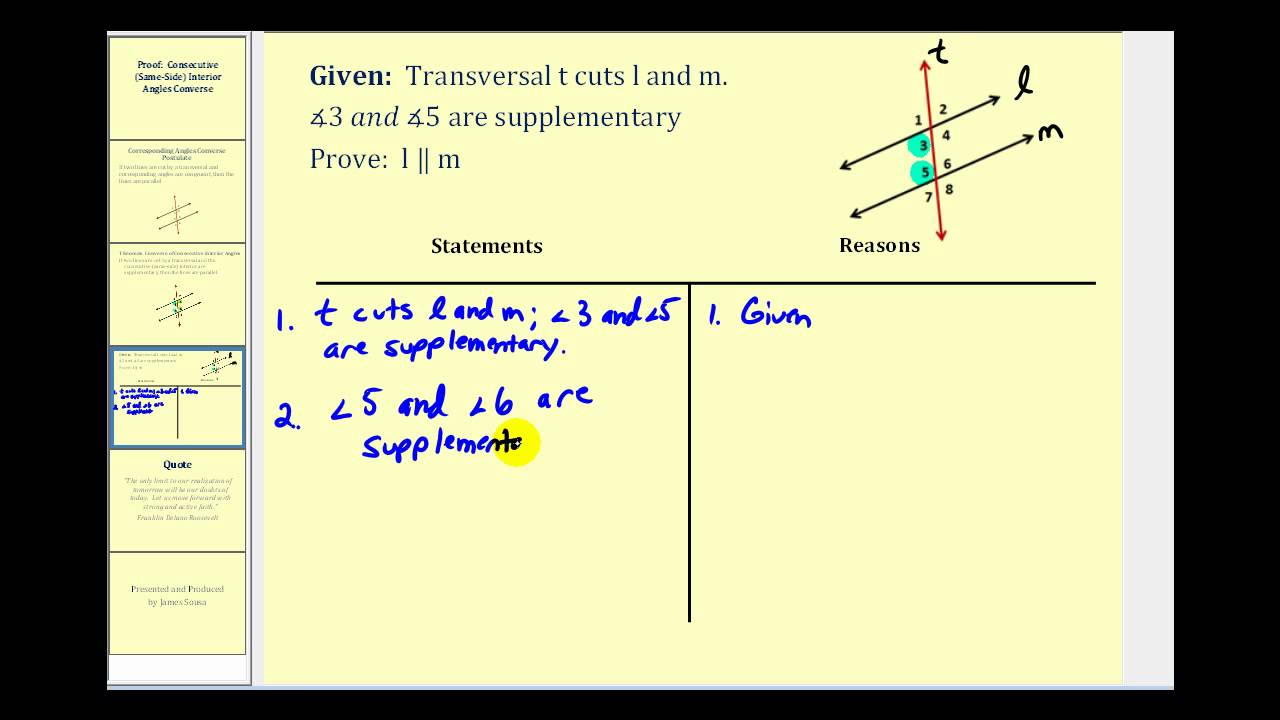
They are equal if the transversal intersects two parallel lines Supplementary angles are seen in three geometry theorems. Definition of linear pair : Two angles that are adjacent and supplementary.Comprises of one interior and one exterior angle.If angle 1 is congruent and supplementary to angle 2, then angles 1 and. Found on the same side of the transversal Theorem 2-5: If two angles are congruent and supplementary, then each is a right angle.The pairs of corresponding angles in the given figure are:Ĭorresponding angles are equal if the transversal intersects at least two parallel lines.Ĭorresponding angles formed when a transversal intersects at least two non-parallel lines are not equal and are also found to have no relation with each other. The above figure shows two parallel lines AB and CD intersected by the transversal GH.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
